High polar and aprotic solvent
DMI™ 1,3 Dimethyl-2-Imidazolidinone
1,3 Dimethyl-2-Imidazolidinone
Applications detail
Applications
Characteristics
- Introduction
- Applications
- Precaution and Packing
DMI, a high purity aprotic solvent, is composed of nitrogen containing five membered ring compound and widely recognized as an epoch making solvent. It is a colorless, transparent, high polar solvent with high thermal and chemical stability and non-corrosiveness. The material has a high boiling point of 222° C, a high flash point of 120° C (open method) / 95° C (close method), and a low melting point of 7.5° C.
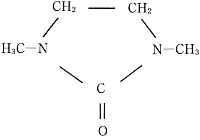
DMI can be used in a variety of applications including detergents, dyestuffs, electronic materials and in the manufacture of polymers. Its versatility can be attributed to it. Of particular note are its excellent solubility for inorganic and organic compounds and high dielectric constant and solvation effect. DMI is also known as 1,3 Dimethyl-2-Imidazolidinone or by CAS number 80-73-9.
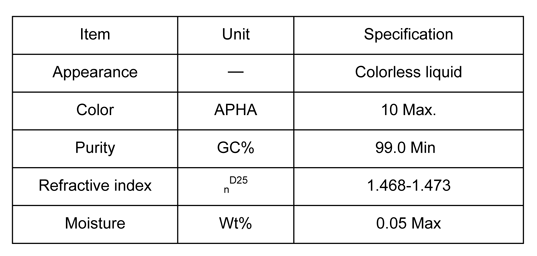
DMI 1,3 Dimethyl-2-Imidazolidinone Specifications
The table on this page provides insight into the appearance, color, purity, refractive index and water content of DMI.
DMI 1,3 Dimethyl-2-Imidazolidinone Physical Properties
- View: Physical Constants Chart
- View: Temperature Dependency of Dielectric Constant, Viscosity, Density and Refractive Index Chart
- View: Hygroscopic Degree of DMI Chart
- View: Drying of DMI Chart
- View: Vapor Pressure Curve of DMI Chart
- View: Freezing Point of the Mixture of DMI and Water Chart
- View: Solubility of Inorganic Compounds in DMI Chart
- View: Solubility of Organic Compounds in DMI (At Room Temperature)
- View: Solubility of Organic Compounds in DMI (At 25°C)
- View: Solubility of Resins in DMI Chart
- View: Explosivity of DMI Chart
- View: Distribution Coefficients of DMI Between Organic Compounds and Water Chart
- View: Solubility Parameter Chart
DMI 1,3 Dimethyl-2-Imidazolidinone Chemical Properties
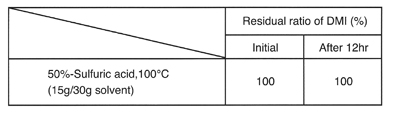
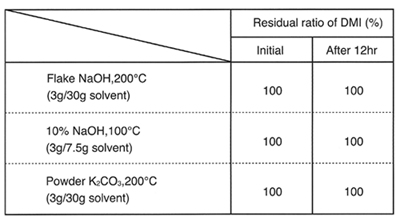
Stability to acids and alkalines
DMI has higher heat stability than general aprotic polar solvents in the presence of acids and alkalines.
Stability in acids (in a stream of N2)
Stability in alkalines (in a stream of N2)
Hydrolysis
Aqueous solution of DMI is not hydrolyzed.
Corrosiveness
DMI does not corrode metallic materials such as iron, steel and stainless steel among others.
Reaction Solvent
As DMI is thermally and chemically stable, its dissolving power for organic and inorganic compounds in addition to its accelerating effect as an aprotic polar solvent, makes it an exceptionally effective reaction solvent. By applying DMI, reaction products of high purity can be obtained in a short time at a higher yield.
It is effective for various nucleophilic substitution reactions such as the synthesis of phenylether derivatives, amino compounds and fluorobenzene derivatives as illustrated below. Its high dielectric constant and solvation effect accelerate anionic nucleophilic reaction through solvation of cations. These synthesis products are used as intermediates in agrochemicals, medicines, dyestuffs and monomers of high performance resins.
Polymers
DMI is uniquely suited for the manufacture of heat resistant thermoplastics and can be effectively used as a solvent for synthesis of various polymers and a cleaning agent for polymerization and molding equipment. In the production of polyamides and polyimides, DMI accelerates the formation of amide and imide groups to produce high molecular weight polymers. In the production of polyphenylenesulfides, products containing smaller amounts of organic impurities are acquired in electric materials. In the production of polyethersulfones, DMI controls side reactions to produce polymers of high quality. In the formation of polyimide and polysulfone films and the stretching of polyetherketone film, treatment of DMI makes films more uniform.
Detergents
By adding DMI to a mixture of surfaceactive agents, alkalines, alcohols, and polyoxyethylenealkylethers, an effective detergent can be obtained. It also makes an effective cleaning solution for glass and metal since it dissolves dirt easily.
Dyestuffs and Pigments
Higher contrast, clear printed images can be obtained by adding DMI as an ink solvent with dyestuffs and pigments.
Electric Materials
Due to its low viscosity and high dielectric constancy, DMI can be used as a solvent for electrolytic solutions of non-aqueous batteries. In addition, it can be used as a stripper for photo-resist, and unlike conventional strippers, does not involve a series of complicated processes because of water insolubility or a resulting adverse impact on the environment.
Surface Treatment Agent
To increase adhesive strength of epoxy resin adhesives, a DMI solution of SDN (polyaryl complex of sodium, potassium or lithium), is used for surface treatment of TEFLON® (polytetrafluoroethylene).
Petroleum Products
DMI has a high boiling point, high thermal stability and doesn't produce azeotrope, therefore it can be used commercially as a solvent in processes such as liquid-liquid extraction, counter current distribution, extractive distillation and counter current washing process.
Since DMI dissolves aromatic compounds, unsaturated hydrocarbons, and does not dissolve paraffin hydrocarbons, it is the best extractant of BTX.
DMI Precaution and Packing
There are various kinds of materials suitable for use in handling DMI. The recommended materials are stainless steel, polyethylene and fluororesins at room temperature. For flange gaskets and gland packing, fluororesins (polytetrafluororesins and other polyfluoroethylenes) are suggested.
DMI is typically stored in iron, can or drum containers whose net weight is 18 kg and 200 kg respectively. DMI has a hygroscopic property and is oxidized more or less when it is exposed to air for a long period of time. Therefore, its storage containers should be kept sealed with inactive gas such as nitrogen.
When handling DMI at low temperature, please note that its melting point is 7.5° C. If the substance touches your skin, remove immediately by washing with water. Exposure to DMI can cause slight irritation as revealed in a test conducted on rabbit's skin. The toxicity of the chemical is as follows:
| LD50 (Mouse Oral) | >300-<2,000 mg/kg |
| LD50 (Rabbit Skin) | 2,000 mg/kg |
| 48 hours TLm | 2,400 ppm |
You should also refer to your local fire prevention regulations, when implementing fire-fighting procedures.
